Artemis is the CLF's facility for ultrafast XUV science. Experiments on Artemis use high harmonics to investigate ultra-fast electron dynamics in condensed matter and gas-phase molecules, and for coherent lensless imaging.
Artemis is based on high repetition rate, multi- and few optical cycle and widely tuneable laser sources, and ultrafast XUV (10-100 eV) pulses produced through high harmonic generation. Vacuum beamlines deliver the synchronised pulses to end-stations for condensed matter physics and gas-phase chemistry. Experiments on Artemis use high harmonic generation to investigate ultrafast dynamics in experiments on gas, liquid and solid materials. We also exploit the spatial coherence of the XUV to use coherent diffractive imaging techniques.
Applications of XUV pulses on Artemis include photoelectron spectroscopy with XUV probe pulses, high harmonic generation spectroscopy, and ultrafast demagnetisation. Artemis aims to combine femtosecond laser and synchrotron technologies to enable new science in the emerging field of ultrafast x-rays.
A key technique used on Artemis is time and angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy, which enables the electronic structure of a material to be monitored as it responds to excitation by a laser pulse. The target material is irradiated by a short laser pulse, which induces structural changes and excitations. It is then probed at a series of time delays by a short wavelength pulse which generates photoelectrons that are then collected and analysed. The Artemis beamline was one of the first in the world to use XUV pulses from high-order laser harmonics for photoemission. The higher photon energy enables electrons with a much wider range of energy and momentum space to be detected, meaning that each snapshot of electronic structure has a much wider field of view.
Artemis is currently being relocated to the Research Complex at Harwell and being upgraded with the addition of a 100kHz OPCPA, an additional beamline and end-stations.
Red Dragon
Topas
Signal (1160 – 1600 nm) – Vertical polarisation
Both outputs available simultaneously
XUV (Broadband)
Output consists of a comb of frequencies separated by twice the driving frequency.
Maximum photon energy and flux depend on driving wavelength.
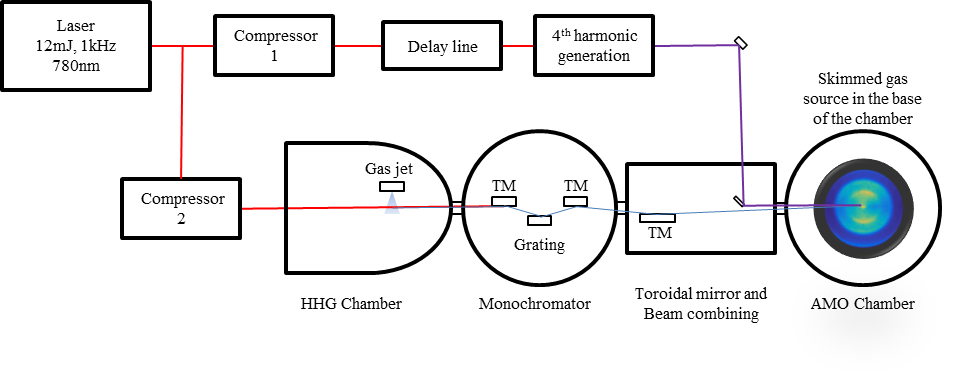
This source can be used with the HHG spectroscopy and XUV imaging end stations.
Different foils (e.g. aluminium, molybdenum selenide) can be used to spectrally filter the radiation to isolate specific spectral regions / reject the fundamental pulse.
XUV (Monochromatised)
This source can be used with the material science and AMO chambers for various types of time-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy techniques.
AMO (Atomic & Molecular Optics)
Time of Flight (ToF)
Sample
Techniques usage
HHG Spectroscopy
Time-of-flight spectrometer
Sample
Material Science
Sample
XUV Imaging
Sample
40mm Imaging MCP
Detection
70mm Imaging MCP
Detection
- Angular Resolved PES
- Spin-resolved ARPES
- Time-resolved studies
- UPS
- Other - Chemistry
- Other - Material Sciences
- Atomic & molecular physics
- Home built in Matlab or Labview
- Raw data
- ASCII text files
Matlab .mat files
- Labview
Matlab
Igor Pro